
|
This page is in the process of a rewrite!
This page is in the process of being rewriten. Some information on this page may differ from how it actually works on Delta-V. A lot of information will be incomplete or may contain placeholders.
You can help Delta-V by expanding it
To-Do: Details, details, details. Someone from #atmos-thread, please!
|

|
Atmospheric Science refers to the observation and processing of gases in enclosed spaces.
The Basics of Atmos
The premise of Atmospherics (or, Atmos) is simple: You want a station that is pressurized and with breathable air, absent of any toxins. The two primary gases used to accomplish that goal are Nitrogen (N2) and Oxygen (O2).
Oxygen is the breathable gas in air, and is respirated by Humans, Onis, Felinids, Arachnids, Moths, Vulpkanins, and Harpies to form Carbon Dioxide (CO2) as a waste gas. Nitrogen, on the other hand, is respirated by Slimes and Voxes instead of Oxygen.
Pressure, measured in kPa, is determined by the amount of gas (in mols) in an area, and is directly related to temperature (in Kelvin or degrees Celsius); so as temperature goes up, so does the pressure. A safe pressure on the station is roughly around 80 to 140 kPa, and a safe temperature is around 20 degrees Celsius. The ideal environment for all species is 22%-25% Oxygen and 78%-75% Nitrogen at 101.325kPa and 20°C (293.15K).
Toxins
Main article: Gases
Toxic gases can bring about many forms of harm to the station, and are dangerous if left unattended because of the tendency of passengers to blindly open doors. These gases are noticeable at high concentrations, as they appear as clouds or smoke. All of these gases are filtered by the scrubber network, and they can be sucked up by Portable Scrubbers considerably faster. To contain the spread of these gases, you’ll want to use Holofan Projectors, inflatable walls or doors, and if need be, you can weld some airlocks closed to prevent entry, just make sure the gas you're dealing with is not flammable.
Pipes, Vents and Other Atmospheric Devices
General Information
All gases can flow through the various pipes found in the game. Gas will always attempt to flow from higher pressure to lower pressure. If a gas is not in a pipe, canister, or tank, it will be in the atmosphere and will interact with other objects.
Gas will always try to even out the pressure. For example, if a empty canister is connected to a pipe pressurized at 4500kpa, the canister will also only be pressurized to 4500kpa. If a canister pressurized at 9000kpa is connected to the same pipe, gas will flow out of the canister until a even pressure is acquired.
If pressurized pipes get unwrenched they will dump all of their contents into the surrounding atmosphere and will, depending on the pressure level, violently blow the wrench user away. You will know if you are unwrenching a pressurized pipe if you get the message stating "A gush of air blows in your face... Maybe you should reconsider?" It is good practice to always use your gas analyzer on every pipe before unwrenching to ensure it is depressurized.
All pipes can be unwrenched to disconnect them from others. By using a welder on a unwrenched pipe segment you can deconstruct it into steel.
A broken or unconnected segment of pipe WILL NOT allow gas to pass through. Do not worry about all your gas escaping out of a broken or unconnected pipe segment.
Most pumps, mixers, and filters do not require power to function. Only air vents and scrubbers require power. You can shift-click on a segment to examine it to see if it is powered.
Pipes
Allows gas to flow freely. Comes in four shapes. Straight, Elbow, 3-way-juntion, 4-way-junction.
| Image
|
Name
|
Description
|

|
gas pipe straight
|
A straight segment of pipe.
|

|
gas pipe bend
|
A elbow segment of pipe.
|

|
gas pipe T junction
|
A three way junction segment of pipe.
|

|
gas pipe fourway
|
A four way junction segment of pipe.
|
Atmospheric Devices
| Image
|
Name
|
Description
|

|
Gas Pump
|
Pumps gas in a specific direction. Has a maximum throughput of 4500 kPa (4.5 Mpa), clogs at 4500 kPa. Loses efficiency as the volume of gas rises. Can be turned on/off to allow/disallow gas flow. Requires power.
|

|
Volumetric Gas Pump
|
Pumps gas based on the mole amount instead of pressure. Has a maximum throughput of 200 L/s, clogs at 9000 kPa (9 Mpa). best used when dealing with extremely high pressure. Requires power.
|

|
Manual Valve
|
Allows gas to flow to and from whatever pipes it's connected to. Can be opened (green light) or closed (red light). Doesn't require power.
|

|
Passive Gate
|
An air valve that's one-way only. The red circle is the inlet part. Does not require power.
|

|
Gas Mixer
|
Allows you to combine the gas flow of two pipes into one. Has a maximum throughput of 4500 kPa, clogs at 4500 kPa. Allows you to set the percentage of throughput of both inputs. The primary port is parallel with the output while the side port is perpendicular. If one input is missing, it will not allow gas flow.
|

|
Gas Filter
|
Filters out a selected gas into another pipeline. Has a maximum throughput of 1000 L/s, clogs at 4500 kPa. Filtered gas will exit out of the perpendicular outlet while all other gases continue to flow down the parallel outlet. The filter outlet will not allow gas flow if no gas is selected or if no pipe is connected to the filter outlet.
|

|
Air Sensor
|
Scans the atmosphere of the tile it's on, shows the information on an air alarm.
|

|
Air Alarm
|
Shows information of the atmosphere in the surrounding area. Allows you to control all the air vents and scrubbers it's connected to. Requires power.
|

|
Gas Vent
|
Used to move gas into the surrounding atmosphere. Can store 4500 kpa but only allows 101.3 kPa to flow out of it. If external pressure is higher than the limit, no gas will flow out of the vent. If external pressure drops too much, the vent will go into under-pressure lockout (shown by the vent having yellow lights instead of blue lights) and no gas will flow out of it. You can right-click on a vent and unlock it from under-pressure lockout after you fix the area. Requires power
|

|
Dual-port Gas Vent
|
Exactly the same as a normal gas vent, but has two input options instead of one. Requires power.
|

|
Passive Vent
|
Allows any pressure and gas to flow in and out of it. Doesn't require power.
|
|
Air Scrubber
|
Slowly siphons selected gases out of the surrounding atmosphere. You can change what gases it siphons via an air alarm. Must be connected to an outlet port to function. Glows blue when working and glows red when in panic mode. Requires power.
|

|
Air Injector
|
inject air into the surrounding atmosphere. Does not allow backflow. Maximum throughput is 9000 kPa, clogs at 9000 kPa. Requires power.
|

|
Pneumatic Valve
|
Has three ports: Control, inlet, an outlit. Allows gas flow like a manual valve, but only if the pressure at the control port is high enough. To turn it on, the control port must be at least 1 atm higher than the lowest pressure connected to the valve. I.E the lesser of the inlet and outlit pressure.
|

|
Canister
|
Used to hold and transport gas without the use of pipes. Use a wrench to connect a canister to a connector port. You can put air tanks into canister to fill them with whatever gas is in the canister.
|

|
Connector Port
|
Used to transfer gas from pipes into canisters. Gas will flow into the canister until pressure evens out between the connector port and the canister. Use gas pumps to force more gas in/out of canisters.
|

|
Gas Miner
|
Creates new gases from nothing, used to make sure stations have an infinite amount of a specific gas. Stations usually only come with an oxygen and nitrogen miner. Found in gas chambers in atmos.
|

|
Gas Recycler
|
Used to recycle carbon dioxide and nitrious oxide into oxygen and nitrogen, respectively. Requires power, 3000 kPa and the gas to be 300°C to work.
|

|
Gas Condenser
|
Condenses an gas into liquid.
|

|
Radiator
|
Used to transfer the temperature of a room to the gas in pipes.
|
 
|
Freezer/heater
|
Connected to pipe networks to heat up the gas inside. Has hellfire variants.
|

|
Portable Scrubber
|
Works just like an air scrubber, but you can pull it around! Anchor it down to have it filter harmful gases out of the air.
|

|
Space Heater
|
A portable heater used to regulate temperatures in certain rooms. Anchor it down and click the interact button to make it work.
|
Design Examples
Pressure Relief Valve
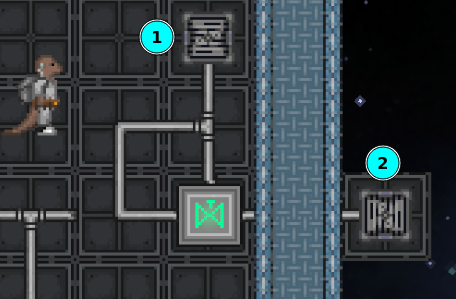
This pressure relief system drains the air inside to space if the pressure exceeds 1 atm, which can be used to guard against accidental station overpressure events. A passive vent inside (1) is connected to the control and the inlet. Another passive vent in space (2) is connected to the outlet. Since the outlet pressure is 0 kPa, then the pneumatic valve will only be on if the inside pressure exceeds 1 atm. When that happens, air from inside is transferred into space until the inside pressure is equal to 1 atm.
Turning Completeness
Pneumatic valves make atmos turing-complete.
Gases

|
This page is a stub!
This page is a stub, meaning it is considered too short, incomplete and/or lacking information about the page's subject.
You can help Delta-V by expanding it.
|

|
Introduction
The gases are the most important part of Atmospherics. There are currently 9 gases in the game, each of them has its own Specific Heat Capacity and Molar Mass. Most of them can be created using Gas Miners or created in combustion reactions.
Gases
Gases in SS14
| Gas |
Description |
Specific Heat Capacity |
Molar Mass (g/mol)
|
Oxygen
 |
Colorless, reactive gas that humans need to breathe to stay alive. Key oxidizing agent in most combustion reactions. |
20 |
32
|
Nitrogen
 |
Colorless, odorless, inert gas. Somehow, slimes and voxes breathe this. |
30 |
28
|
Carbon Dioxide
 |
Colorless, odorless, relatively inert gas. Exhaled by creatures that breathe oxygen. Toxic in high enough quantities. The reason why atmospheric technicians are employed. |
30 |
44
|
Plasma
 |
Purple, putrid, highly-combustible, and toxic gas. Combusts in the presence of oxygen, but will not ignite on its own. Unfortunately, it is also vitally important to industrial and scientific activities aboard Nanotrasen stations. |
200 |
120
|
Tritium
 |
Green, highly-combustible, and radioactive. Combusts in the presence of oxygen. It is formed by the combustion of Oxygen and Plasma. To form Tritium, there must be 96 times more Oxygen than Plasma during the reaction. If there is too much Plasma, the reaction will produce Carbon Dioxide instead. |
10 |
6
|
Water Vapor
 |
Water in gaseous form. Due to the unique environment of space, does not condense into liquid water. Harmful to slime people. |
40 |
18
|
Miasma
 |
Purple, foul-smelling gas. Breeds disease, toxic, and harmful in sufficiently large concentrations. A by-product of nasty biological processes, including rotting bodies. |
20 |
44
|
Nitrous Oxide
 |
Colorless, Otherwise known as "laughing" or "sleepy" gas, it acts as a sedative to non-slimes and is toxic in very high concentrations. Unfortunately, this stuff is exhaled by slimes. Formed from Frezon and Nitrogen |
40 |
44
|
Frezon
 |
Blue-greenish gas. Used as an industrial coolant. Used recreationally by some for its euphoric effects, before their lungs freeze out. It has a high value and is made by mixing cold Tritium and Oxygen. |
600 |
50
|






























